

However, improvements in neuroimaging have helped to make better distinctions between tumor types and between tumor and normal cells. GBM’s capacity to wildly invade and infiltrate normal surrounding brain tissue makes complete resection impossible. A supportive family environment is also helpful. Treatment requires effective teamwork from neurosurgeons, neuro-oncologists, radiation oncologists, physician assistants, social workers, psychologists, and nurses. If inoperable, then radiation or radiation/chemotherapy can be administered. Standard treatment is surgery, followed by radiation therapy or combined radiation therapy and chemotherapy. GBM accounts for 12% to 15% of all intracranial tumors and 50% to 60% of astrocytic tumors. The incidence, or the number of new diagnoses made annually is 2 to 3 per 100,000 people in the United States and Europe. The cause is unknown, but increasingly research is pointing toward genetic mutations.Median survival rate of ~15 months 5-year survival rate of ~4%.
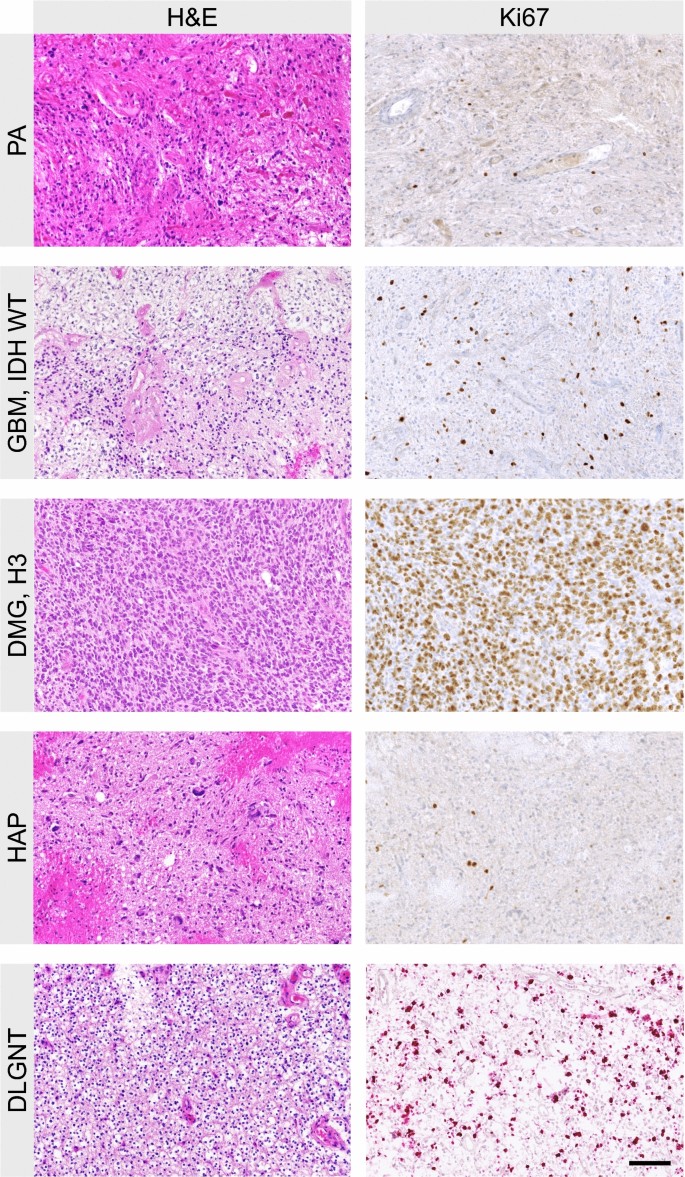 Most common in older individuals and more common in men than women. Can develop directly or evolve from lower grade astrocytoma or oligodendroglioma. Can be composed of several different cell types. Parallel research at Johns Hopkins University also contributed to the expansion of genomic information on GBM. In this effort, researchers discovered that GBM has four distinct genetic subtypes that respond differently to aggressive therapies, making treatment extremely difficult and challenging. GBM develops primarily in the cerebral hemispheres but can develop in other parts of the brain, brainstem, or spinal cord.īecause of its lethalness, GBM was selected as the first brain tumor to be sequenced as part of The Cancer Genome Atlas ( TCGA Website), a national effort to map the genomes of the many types of cancer. Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is the most common and deadliest of malignant primary brain tumors in adults and is one of a group of tumors referred to as gliomas.Ĭlassified as a Grade IV (most serious) astrocytoma, GBM develops from the lineage of star-shaped glial cells, called astrocytes, that support nerve cells.
Most common in older individuals and more common in men than women. Can develop directly or evolve from lower grade astrocytoma or oligodendroglioma. Can be composed of several different cell types. Parallel research at Johns Hopkins University also contributed to the expansion of genomic information on GBM. In this effort, researchers discovered that GBM has four distinct genetic subtypes that respond differently to aggressive therapies, making treatment extremely difficult and challenging. GBM develops primarily in the cerebral hemispheres but can develop in other parts of the brain, brainstem, or spinal cord.īecause of its lethalness, GBM was selected as the first brain tumor to be sequenced as part of The Cancer Genome Atlas ( TCGA Website), a national effort to map the genomes of the many types of cancer. Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is the most common and deadliest of malignant primary brain tumors in adults and is one of a group of tumors referred to as gliomas.Ĭlassified as a Grade IV (most serious) astrocytoma, GBM develops from the lineage of star-shaped glial cells, called astrocytes, that support nerve cells.






 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
